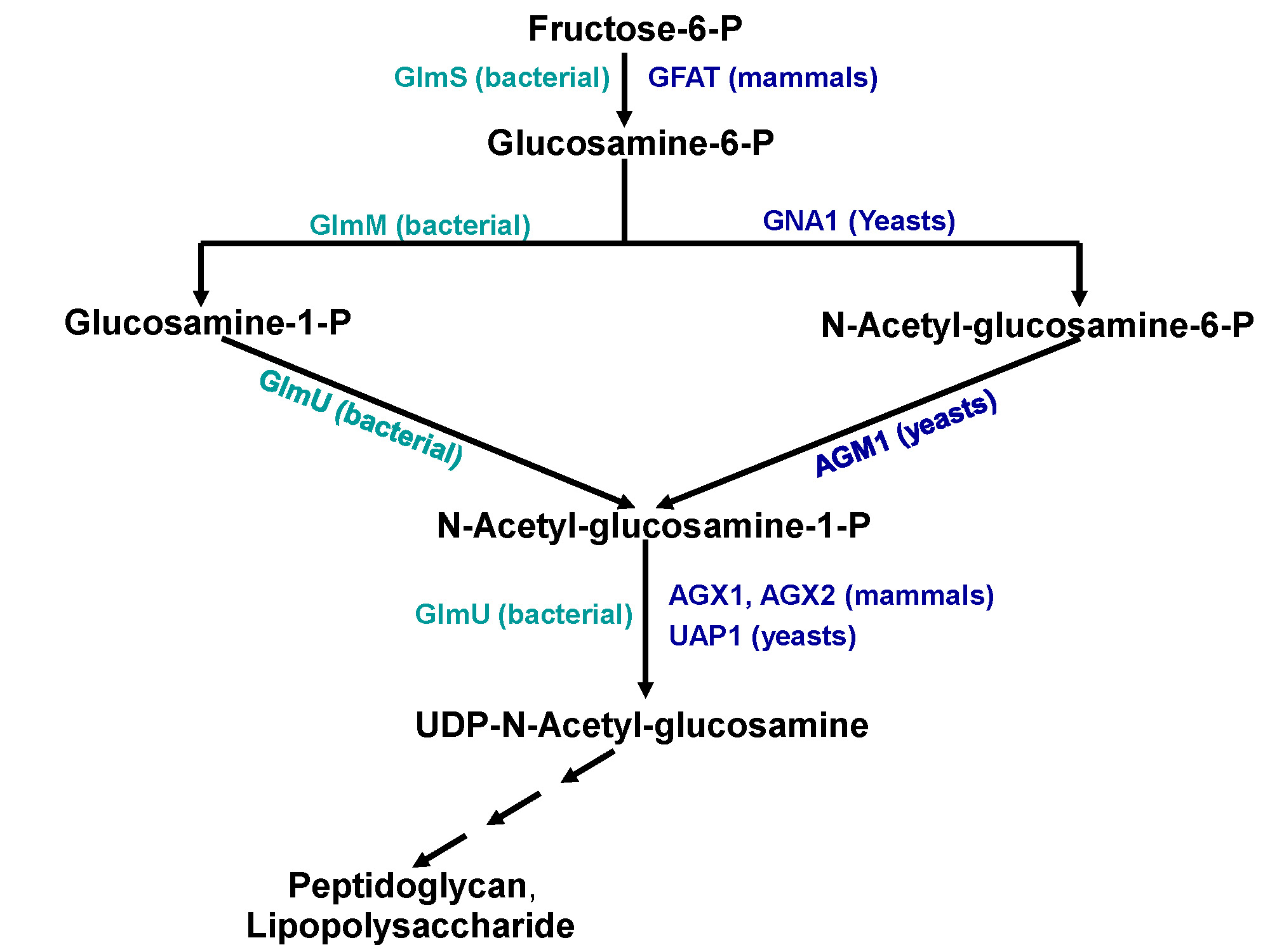
 Figure shows the importance of Glmu protein in cell wall synthesis pathway. Left side shows ezymes presents in prokaryotes and right side shows enzyme in eukaryotes. |
A open source Webserver for prediction of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (M.Tb) inhibitors using QSAR and Docking statergies.GDoQ web server has been developed to serve scientific community working in the field of Drug Desigining for designing inhibitors against N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate uridyltransferase (GLMU) protein, a potential drug target involved in bacterial cell wall synthesis. This server uses molecular docking and QSAR strategies to predict inhibitory activity value (IC50) of chemical compounds for GLMU protein. The algorithm behind the server includes the docking of compounds into the active site of enzyme followed by QSAR modeling where, docking generated energy based scoring values (for the best conformer), v-life descriptor and Web-Cdk descriptors are used as input variables to QSAR based Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) model for prediction of IC50 value. The QSAR model implemented on the server has been trained on the diverse dataset of 84 inhbitors of GLMU Protein and predict the IC50 value with correlation R/R2 values of 0.79/0.62. |